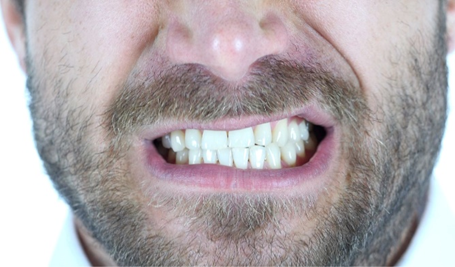
What is Bruxism (Teeth Clenching) ?
Clenching of teeth, also known as bruxism, is a common condition characterized by the involuntary grinding, clenching, or gnashing of teeth. It can occur during the day (awake bruxism) or at night (sleep bruxism) and can lead to various dental problems if left untreated.
Causes of Bruxism
- Stress and anxiety: Bruxism is often associated with psychological stress and anxiety.
- Sleep disorders: Conditions like sleep apnea or snoring can contribute to bruxism.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and caffeine intake can increase the risk of bruxism.
- Psychological factors: Emotions like anger, frustration, or tension can trigger bruxism episodes.
- Abnormal bite or jaw development: Developmental abnormalities in the jaw or bite can contribute to bruxism.
Symptoms of Bruxism
Recognizing the symptoms of teeth Clenching is crucial for early intervention.
Common signs include:
- Persistent jaw pain or soreness
- Headaches, especially in the temples
- Tooth sensitivity or pain
- Worn-down tooth enamel
- Disrupted sleep patterns
Types of Bruxism
Clenching of Teeth can be classified into two main types
- Awake bruxism
- Sleep bruxism
Awake Bruxism:
Clenching teeth while awake, also known as awake bruxism, often occurs subconsciously during periods of stress or concentration. It can lead to similar symptoms as sleep bruxism and may require similar management techniques to prevent long-term damage to the teeth and jaw.

Sleep Bruxism:
Sleep bruxism occurs during sleep and is often more challenging to control since it happens involuntarily. Using a mouthguard or splint while sleeping can help protect the teeth from damage caused by grinding and alleviate associated symptoms like jaw pain and headaches.
Is Clenching Your Teeth Serious?
While occasional teeth clenching may not cause significant harm, persistent or severe bruxism can lead to serious dental issues such as fractured teeth, TMJ disorders, and chronic pain. It’s essential to address bruxism early on to prevent long-term complications.
Teeth Clenching in Children
Teeth Clenching is not uncommon in children, particularly during periods of teething or jaw growth. Most children outgrow bruxism by adolescence without any long-term consequences. However, if teeth clenching persists or causes significant discomfort, it’s essential to consult a paediatric dentist for evaluation and management strategies.
How to Stop Bruxism (Teeth Clenching) – Naturally ?
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing and meditation
- Use a warm compress on your jaw muscles to alleviate tension.
- Avoid chewing gum or tough foods excessively
- Establish a bedtime routine to promote better sleep habits.
- Try massaging your jaw muscles to relieve tension.
Teeth Clenching Treatment
Treatment for teeth clenching varies depending on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, lifestyle modifications and natural remedies may be sufficient.
In more severe instances, interventions such as the following may be necessary:
- Dental correction for misaligned teeth
- Stress management techniques
- Behavioural therapy
- Prescription medications for underlying sleep disorders or anxiety
Clenching of Teeth is a prevalent condition that can have significant implications for oral health and overall well-being. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to manage bruxism effectively and preserve their dental health. If you suspect you or your child may be Clenching their teeth, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance from a dentist or healthcare provider.




